Database management
system is a collection of programs that enables user to store , retrieve ,
update and delete information from a database .
Relational Database
Management system (RDBMS) is a database management system (DBMS) that is based
on the relational model . Data from relational database can be accessed or
reassembled in many different ways without having to reorganize the database
tables . Data from relational database can be accessed using a API , Structured
Query Language (SQL)
Structured Query
Language(SQL) is a language designed specifically for communicating with
databases. SQL is an ANSI (American National Standards Institute) standard .
4.
What are the different type of Sql's?
1. DDL – Data Definition Language
DDL is used to define
the structure that holds the data. For example. table
2. DML – Data Manipulation Language
DML is used for
manipulation of the data itself. Typical operations are Insert,Delete,Update
and retrieving the data from the table
3. DCL – Data Control Language
DCL is used to control
the visibility of data like granting database access and set privileges to
create table etc.
5.
What are the Advantages of SQL
- SQL is not a proprietary language used by specific database vendors. Almost every major DBMS supports SQL, so learning this one language will enable programmer to interact with any database like ORACLE, SQL ,MYSQL etc.
- SQL is easy to learn. The statements are all made up of descriptive English words, and there aren't that many of them.
- SQL is actually a very powerful language and by using its language elements you can perform very complex and sophisticated database operations.
6.
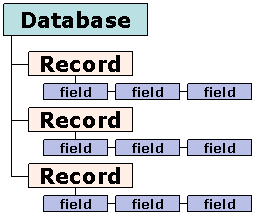
what is a field in a database ?
A field is an area
within a record reserved for a specific piece of data. Examples: Employee Name
, Employee ID etc
A record is the
collection of values / fields of a specific entity: i.e. a Employee , Salary
etc
A table is a
collection of records of a specific type. For example, employee table , salary
table etc .
SQL Interview Questions on Database Transactions
9.
What is a database transaction?
Database transaction
take DB from one consistent state to another. At the end of the transaction the
system must be in the prior state if transaction fails or the status of the
system should reflect the successful completion if the transaction goes
through.
10.
What are properties of a transaction?
Properties of the
transaction can be summarized as ACID Properties.
1. Atomicity
In this , a
transaction consists of many steps. When all the steps in the transaction go
completed it get reflected in DB or if any step fails, all the transactions are
rolled back.
2. Consistency
The database will move
from one consistent state to another if the transaction succeeds and remain in
the original state if the transaction fails.
3. Isolation
Every transaction
should operate as if it is the only transaction in the system
4. Durability
Once a transaction has
completed successfully, the updated rows/records must be available for all
other transactions on a permanent basis
11.
What is a Database Lock?
Database lock tell a
transaction if the data item in questions is currently being used by other
transactions.
12.
What are the type of locks?
1. Shared Lock
When a shared lock is
applied on data item, other transactions can only read the item, but cant write
into it.
2. Exclusive Lock
When a exclusive lock
is applied on data item, other transactions cant read or write into the data
item.
SQL Interview Questions on Database
Normalization
13.
What are the different type of normalization?
In database design ,
we start with one single table, with all possible columns. Lot of redundant
data would be present since it’s a single table. The process of removing the
redundant data, by splitting up the table in a well defined fashion is called
normalization.
1. First Normal Form
(1NF)
A relation is said to
be in first normal form if and only if all underlying domains contain atomic
values only. After 1NF , we can still have redundant data
2. Second Normal Form
(2NF)
A relation is said to
be in 2NF if and only if it is in 1NF and every non key attribute is fully
dependent on the primary key. After 2NF , we can still have redundant data
3. Third Normal Form
(3NF)
A relation is said to
be in 3NF if and only if it is in 2NF and every non key attribute is
non-transitively dependent on the primary key
SQL Interview Questions on Database Keys and
Constraints
14.
What is a primary key?
A primary key is a
column whose values uniquely identify every row in a table. Primary key values
can never be reused. If a row is deleted from the table, its primary key may
not be assigned to any new rows in the future. In the examples given below
“Employee_ID” field is the primary key .
1. To define a field as primary key, following conditions had to
be met :
2. No two rows can have the same primary key value.
3. Every row must have a primary key value
4. Primary key field cannot be null
5. Values in primary
key columns can never be modified or updated.
15.
What is a SQL Composite Primary Key
A Composite primary
key is a set of columns whose values uniquely identify every row in a table.
For example , in the table given above , if "Employee_ID" and
"Employee Name" together uniquely identifies a row its called a
Composite Primary Key . In this case , both the columns will be represented as
primary key .
16.
What is a Composite Primary Key ?
A Composite primary
key is a set of columns whose values uniquely identify every row in a table.
For example , in the table given above , if "Employee_ID" and
"Employee Name" together uniquely identifies a row its called a
Composite Primary Key . In this case , both the columns will be represented as
primary key .
17.
What is a Foreign Key ?
When a "one"
table's primary key field is added to a related "many" table in order
to create the common field which relates the two tables, it is called a foreign
key in the "many" table. In the example given below , salary of an
employee is stored in salary table . Relation is established via foreign key
column “Employee_ID_Ref” which refers “Employee_ID” field in Employee table .
18.
What is a Unique Key ?
Unique key is same as
primary with difference being existence of null . Unique key field allows one
value as NULL value .
SQL Interview Questions on SQL Commands
19.
Define SQL Insert Statement?
SQL INSERT statement
is used to add rows to a table. For a full row insert , SQL Query should start
with “insert into “ statement followed by table name and values command
followed by the values that need to be inserted into the table .Insert can be
used in several ways:
1. To insert a single complete row
2. To insert a single
partial row
20.
Define SQL Update Statement?
SQL Update is used to update data in a row or set of rows
specified in the filter condition .
The basic format of an
SQL UPDATE statement is ,Update command followed by table to be updated and SET
command followed by column names and their new values followed by filter
condition that determines which rows should be updated
21.
Define SQL Delete Statement?
SQL Delete is used to
delete a row or set of rows specified in the filter condition .The basic format
of an SQL DELETE statement is ,DELETE FROM command followed by table name
followed by filter condition that determines which rows should be updated
22.
What are wild cards used in database for Pattern Matching ?
SQL 'Like' search takes more time to process . So before using
like operator following tips should be considered .
Don't overuse wild cards. If another search operator will do,
use it instead.
When you do use wild cards, try to not use them at the beginning
of the search pattern unless absolutely necessary. Search patterns that begin
with wild cards are the slowest to process.
Pay careful attention
to the placement of the wild card symbols. If they are misplaced, you might not
return the data you intended
SQL Interview Questions on SQL Joins
23.
Define Join and explain different type of joins?
In order to avoid data
duplication , data is stored in related tables . Join keyword is used to fetch
data from related table. Join return rows when there is at least one match in
both tables . Type of joins are
Right Join
Return all rows from the right table, even if there are no
matches in the left table .
Outer Join
Left Join
Return all rows from the left table, even if there are no
matches in the right table .
Full Join
Return rows when there
is a match in one of the tables .
24.
What is Self-Join?
Self-join is query
used to join a table to itself. Aliases should be used for the same table comparison.
25.
What is Cross Join?
Cross Join will return
all records where each row from the first table is combined with each row from
the second table.
SQL Interview Questions on Database Views
26.
What is a view?
Views are virtual
tables. Unlike tables that contain data, views simply contain queries that
dynamically retrieve data when used.
27.
What is a materialized view?
Materialized views is
also a view but are disk based . Materialized views get updated on specific
duration, base upon the interval specified in the query definition. We can
index materialized view.
28.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of views in a database?
Advantages:
1. Views doesn't store data in a physical location.
2. View can be use to hide some of the columns from the table
3. Views can provide
Access Restriction, since data insertion , updation and deletion is not
possible on the view.
Disadvantages:
1. When a table is dropped , associated view become irrelevant.
2. Since view are created when a query requesting data from view
is triggered, its bit slow
3. When views are
created for large tables, it occupy more memory .
SQL Interview Questions on Stored Procedures and
Triggers
29.
What is a stored procedure?
Stored Procedure is a
function which contain collection of SQL Queries. Procedure can take inputs ,
process them and send back output.
30.
What are the advantages a stored procedure?
Stored Procedures are
precomplied and stored in database. This enable the database to execute the
queries much faster. Since many queries can be included in a stored procedure,
round trip time t o execute multiple queries from source code to database and
back is avoided.
31.
What is a trigger?
Database are set of
commands that get executed when an event(Before Insert,After Insert,On
Update,On delete of a row) occurs on a table,views.
32.
Explain the difference between DELETE , TRUNCATE and DROP commands?
Once delete operation
is performed Commit and Rollback can be performed to retrieve data. But after
truncate statement, Commit and Rollback rollback statement cant be performed.
Where condition can be used along with delete statement but it cant be used
with truncate statement. Drop command is used to drop the table or keys like
primary,foreign from a table.
33.
What is the difference between Cluster and Non cluster Index?
A clustered index
reorders the way records in the table are physically stored. There can be only
one clustered index per table. It make data retrieval faster. A non clustered
index does not alter the way it was stored but creates a complete separate
object within the table. As a result insert and update command will be faster.
34.
What is Union, minus and Interact commands?
MINUS operator is used
to return rows from the first query but not from the second query. INTERSECT
operator is used to return rows returned by both the queries.




No comments:
Post a Comment